The scapula is a three-dimensional triangular bone that connects the humerus and the collarbone. It owes its name to the external resemblance to a well-known tool: a garden shovel. The hollow of the scapula and the head of the humerus form the shoulder joint, which is the most flexible joint in the human skeleton.
Pain under the right shoulder blade from the back from the back in most cases indicates the pathology of the joint elements of the shoulder, spine or paravertebral (paravertebral) structures. Other possible causes are damage to internal organs: bronchi, lungs, kidneys and gallbladder. Persistent pain syndrome in the shoulder blade area almost always indicates a serious problem that requires medical and sometimes surgical treatment.
Muscle strain and inflammation
A large number of muscles are attached to the scapula: subscapularis, coracohumeral, small and large rhomboid, deltoid. Most often it hurts under the right shoulder blade because a strain has occurred or an inflammatory process develops.
Muscle stretching can cause severe stress on the back, lifting and carrying of weights, sudden movements and prolonged uncomfortable position of the body. However, as practice shows, in more than half of cases, the cause is excessive physical exertion by an unprepared person and improper exercise.
Symptoms of a stretch are as follows:
- acute pain of varying intensity;
- increased pain when turning and tilting the body;
- relief during rest;
- swelling and bruising (with severe damage).
The basic principle of the treatment of sprains is complete rest and the elimination of any stress. Immediately after the injury, it is necessary to apply ice or a cold compress to the sore spot, if necessary, take an anesthetic pill.
With muscle inflammation - myositis - concerns about aching pain, which increases with pressure and movement. Sometimes there is a slight swelling and redness. Often the general condition worsens: the body temperature rises, the head hurts, and painful small seals are felt in the muscles.
The causes of myositis are different, but most often it develops against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, flu or tonsillitis. It should be noted that in the thoracic region, the muscles become inflamed relatively rarely, since myositis is localized mainly in the upper back or lower back.
One of the varieties is myositis or ossifying fibrodysplasia, an extremely rare form of the disease. This congenital disorder of osteogenesis (bone formation) develops rapidly and occurs in childhood.
Fibrodysplasia is the formation of ossified points in the muscle structure that gradually enlarge and damage the surrounding tissue. The process of ossification (ossification) can be located almost anywhere: near the spine, on the limbs or in the pelvic region.
Reference:ossifying myositis is incurable and does not even lend itself to surgical treatment. After the removal of the ossifications, they are formed again.
Myofascial syndrome
Muscle pain in the back is the most common after headache. More than 40% of people suffer from chronic pain syndrome, most of which are women.
Myofascial syndrome is a progressive condition characterized by the formation of trigger points (pains) in the muscles. The diameter of each point varies from 1 to 3 mm, the accumulation of points can create a painful area of 1 cm2. These points are formed under the influence of trauma and muscle strains.
A number of factors can provoke this process:
- skeletal abnormalities - scoliosis (curvature of the spine to the left or right), pelvic asymmetry, shortening of one of the limbs, flat feet;
- back injuries;
- diseases of the spine - osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, as well as hernia and protrusion;
- long-term use of drugs - -blockers, cardiac glycosides, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, anesthetics;
- damage to connective tissue in autoimmune diseases - rheumatism, lupus erythematosus.
cholelithiasis
With gallbladder pathologies, pain often radiates to the right shoulder blade. This is due to a spasm of smooth muscle when the walls of the bladder are irritated by the stones formed (stones). An attack of biliary colic occurs, as a rule, suddenly and focuses on the right side under the ribs.
The pain syndrome has a sharp and cutting character and in most cases occurs after consuming fatty, fried, spicy foods, alcoholic beverages. The cause of an attack can be heavy physical exertion, nervous exertion or a prolonged incline position.
If there is a blockage in the bile duct, the pain is perceived as dull and drawing. A concomitant symptom is heaviness in the abdomen on the right, as well as nausea, which turns into vomiting. An increase in body temperature is possible, sometimes to high values. With blockage of the common bile duct and obstruction of the sphincter of Oddi, jaundice develops and stool becomes discolored.
Treatment of gallstone disease can be conservative and surgical. In the absence of complications, specific therapy is not performed. Individual stones can be removed by shock wave lithotripsy.
Subphrenic abscess
Back pain in the shoulder blade area can be explained by the formation of a subphrenic abscess - an abscess located under the dome of the diaphragm. Most often, it appears after abdominal surgery, when peritonitis develops. The causative agent can be staphylococcus, streptococcus or E. coli.
Infection enters the body after partial or complete removal of the stomach, resection of the pancreas, suturing of the perforated ulcer, removal of the spleen. The cause can be inflammatory pathology of internal organs, open or closed abdominal trauma, as well as severe lung injuries, osteomyelitis of the vertebral and rib bones.
The first general symptoms appear: weakness, sweating and fever. The rise in body temperature can be maintained constantly or increase periodically. Then it begins to hurt in the upper third of the abdomen and lower chest on the affected side. Pain syndrome of varying intensity often radiates under the scapula, shoulder, or collarbone.
A characteristic sign of an abscess is shortness of breath, dry cough, hiccups, and increased pain when moving, taking a deep breath, coughing and sneezing. The patient breathes frequently and superficially, tries to assume a semi-sitting position.
Treatment of subphrenic abscess consists of surgical opening and drainage of the abscess, after which antibacterial, anti-intoxication, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy is performed.
Reference:if the operation is not performed in time, the abscess breaks into the abdominal and pleural cavities, which guarantees a near-lethal outcome.
Pleurisy
Pain near the shoulder blade can cause bronchopulmonary diseases - pneumonia or bronchitis, complicated by pleurisy. In this case, it can hurt both below and above the shoulder blade. However, the main source of pain is the chest and upper abdomen.
Pleurisy is always a complication of another disease, including malignant neoplasms. It can be caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection, trauma, and chest surgery.
In some cases, pleurisy develops against the background of autoimmune diseases - scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, as well as pulmonary thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, pancreatitis.
In 25% of patients with pleurisy, a malignant tumor is diagnosed: mesothelioma or metastases from other organs (mammary gland, ovaries). Metastatic pleurisy usually has mild symptoms and often occurs only with pains behind the breastbone.
When a large amount of exudate accumulates, it is necessary to puncture for its evacuation or drainage. Depending on why pleurisy developed, specific treatment is prescribed. It can include antibiotics, steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs. The form of tuberculosis is treated with special drugs.
Urolithiasis disease
The formation of stones in the urinary system most often occurs in middle-aged people - from 25 to 50 years old. The disease proceeds in different ways: in some the symptoms are limited to a single unpleasant episode, while others complain of regular exacerbations. In some cases, urolithiasis has a chronic and prolonged course.
The main symptom is renal colic when the ureter is blocked. The localization of the pain syndrome depends on the location of the stone, and the intensity depends on its size. Right shoulder blade pain occurs when the right kidney is affected. If the stone is lower, it hurts the lower back or lower abdomen.
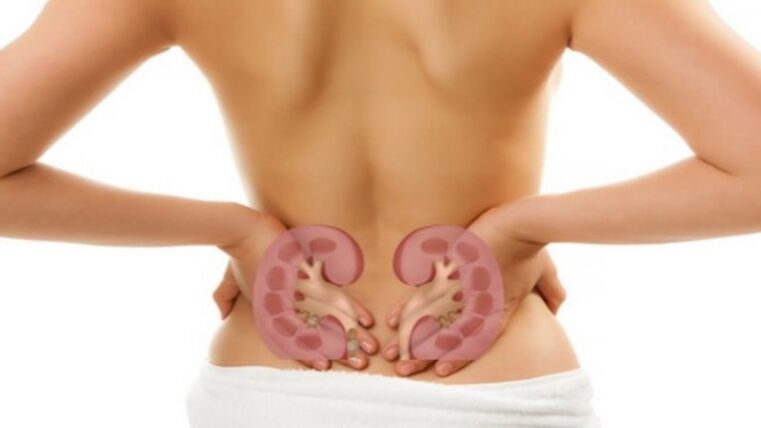
Typical symptoms of urolithiasis are frequent urgency and a burning sensation when urinating, fever and nausea.
The method of treatment can be conservative and surgical. Most often an operation is required, the indications for its implementation are:
- large stones;
- the development of renal failure;
- localization of the stone in the kidney, renal pelvis or ureter;
- purulent pyelonephritis.
Surgery can be open or endoscopic. Shock wave lithotripsy is the gentlest method to reduce the rate of postoperative complications.
During the operation, the stones are crushed by means of a reflector that emits electro-hydraulic waves. After crushing, the stone particles and sand are excreted in the urine. Sometimes their movement along the ureter causes renal colic, which can be easily stopped with drugs.
Reference:any operation is not a guarantee of absence of relapses. Therefore, complex therapy is necessarily carried out, which can last for several years.
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia (thoracalgia) is characterized by severe symptoms and most often manifests itself with sharp, piercing pain in the ribs, both in the front and in the back. It can appear intermittently or disturb constantly. The pain syndrome is aching, burning, or dull, but always difficult to bear.
A characteristic sign of neuralgia is a sharp increase in pain when inhaling, changing the position of the body or sneezing. Often, during a painful attack, the muscles contract, sweating increases, the skin turns red or, conversely, turns pale. Numbness occurs at the site of damage to the nerve endings.
The immediate cause of the pathology is pinching of the nerve roots, which is facilitated by various factors and diseases:
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylitis;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- primary and metastatic tumors;
- stomach disruption (gastritis);
- age-related changes in blood vessels;
- metabolic disease;
- chest trauma;
- flu, SARS;
- hypothermia and drafts;
- prolonged or severe nervous stress;
- high physical activity;
- unsuccessful rotation of the body, prolonged stay in a static position.
Reference:intercostal neuralgia is characterized by pain lasting from a few seconds to three minutes. During this period, the patient tries not to breathe or move, so as not to increase the pain.
The main direction of treatment is the relief of pain syndrome, for which non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed. For severe pain, therapeutic blocks with anesthetics and steroids are performed. To increase the excitability threshold of the CNS, sedatives are used.
Specific therapy depends on the origin of the neuralgia and can include antivirals, antihistamines and muscle relaxants.
neoplasms
Bone tumors of the scapula are very rare and can be both benign and malignant. The first include osteoma and chondroma, the second - chondrosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma. Osteoma is characterized by slow growth and a favorable course. It mainly affects children and young people aged 5 to 20 years.
Osteoma can grow asymptomatically and occur only when surrounding structures - nerve roots and blood vessels - are compressed. Treatment is only surgical, there are practically no relapses.
Chondroma is a benign tumor that arises from cartilage tissue. It should be noted that when the chondroma is localized in the scapula, the tumor often degenerates into malignant. Due to the high risk of malignancy, such formations are radically removed.
Chondrosarcoma, like chondroma, is made up of cartilage tissue but is malignant and widespread. Its growth is accompanied by increased pain and swelling in the affected area.
Chondrosarcoma occurs in people of any age, even in children, but the largest percentage is in middle age, from 40 to 60 years old. Most men suffer. The main method of treatment is the removal of the tumor, if it is impossible to perform the operation, then chemotherapy and radiotherapy are performed.
Ewing's sarcoma is one of the most aggressive malignancies prone to early metastasis. It affects children and young people, is manifested by severe symptoms: pain, swelling and redness.
Since the tumor is highly aggressive, both surgical and therapeutic treatment is performed. Both before and after the operation, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are performed, and with the use of high doses and different drugs. The prognosis of the disease is conditionally poor.
Pain under the right shoulder blade can be a completely harmless symptom or indicate a serious illness. To eliminate pain and prevent possible complications, a specialist consultation and examination is required. Based on its results, the doctor will prescribe treatment and give the necessary recommendations. Be healthy!




































